C38 atom bomb The C38 atom bomb, also known as the “Mark 38” or “Fat Man” bomb, was a type of implosion-type fission bomb developed by the United States during World War II. It was one of the most powerful weapons ever created, with an explosive yield of approximately 21 kilotons of TNT, equivalent to the energy released by about 15,000 tons of TNT.
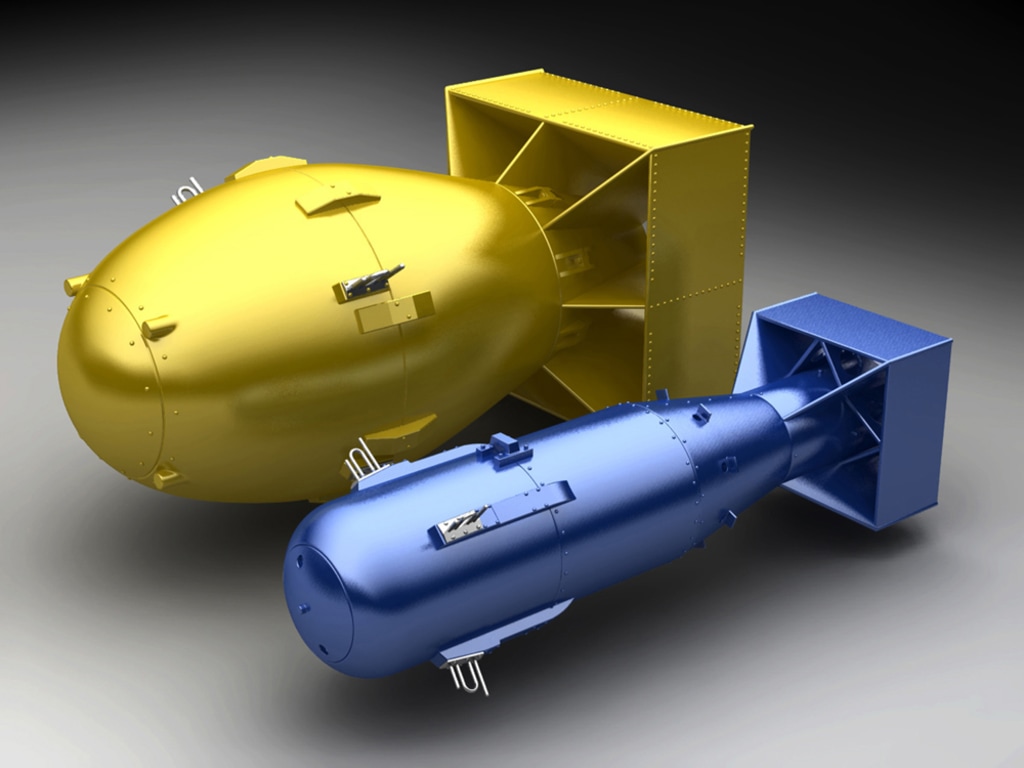
Development of the C38 Atom Bomb
The C38 atom bomb was developed by scientists and engineers at the Los Alamos Laboratory in New Mexico as part of the Manhattan Project, a top-secret research and development program aimed at creating an atomic bomb before the Germans could do so. The bomb’s design was based on the implosion method, which used a high-explosive charge to compress a plutonium core, causing it to undergo a rapid nuclear fission reaction and release a tremendous amount of energy.
Characteristics of the C38 Atom Bomb
The C38 atom bomb was a large, spherical device weighing approximately 6,200 pounds (2,800 kg) and measuring 32 inches (81 cm) in diameter. It was encased in a thick steel casing and had a tail assembly that housed the bomb’s firing mechanism and tail fins for stabilization during flight.

Deployment of the C38 Atom Bomb
The C38 atom bomb was only used twice in combat, both times against Japanese cities during the final stages of World War II. On August 6, 1945, a C38 bomb codenamed “Little Boy” was dropped on the city of Hiroshima, Japan, killing an estimated 70,000 people and destroying much of the city. Three days later, on August 9, 1945, another C38 bomb codenamed “Fat Man” was dropped on the city of Nagasaki, Japan, killing an estimated 40,000 people and causing widespread destruction.
MUST READ=fortitude of the nightborne armor set
The Legacy of the C38 Atom Bomb
The use of the C38 atom bomb against Hiroshima and Nagasaki had a profound impact on the world, marking the beginning of the nuclear age. The bombings demonstrated the immense destructive power of nuclear weapons and raised questions about the ethics of using such weapons in war. The bombings also led to the development of nuclear deterrence, a strategy in which countries maintain powerful nuclear arsenals to prevent nuclear attacks.
The C38 atom bomb remains a controversial weapon, with some arguing that its use was justified in order to bring a swift end to World War II and save countless lives, while others argue that it was an act of barbarity that caused unnecessary suffering and death.
Conclusion
The C38 atom bomb was a powerful and destructive weapon that played a significant role in the history of warfare. Its use against Hiroshima and Nagasaki had a profound impact on the world, marking the beginning of the nuclear age and raising important ethical questions about the use of nuclear weapons. The C38 atom bomb remains a controversial weapon, with its legacy still debated today.


